Percentage of Aborted Babies That Are Endangering the Mother
| Key Takeaways |
|
Introduction
Abortions occurring at or after 21 weeks gestational age are rare. They are frequently difficult to obtain, as they are typically costly, fourth dimension-intensive and but performed by a small-scale subset of abortion providers. Yet these abortions receive a disproportionate amount of attention in the news, policy and the law, and discussions on this topic are oft fraught with misinformation; for instance, intense public discussions take been sparked afterwards several policymakers have theorized virtually abortions occurring "moments before nativity" or even "after birth." In reality, these scenarios do not occur, nor are they legal, in the U.S. Word of this topic is further obscured due to the terms sometimes used to depict abortions afterwards in pregnancy– including "late-term," "postal service-viability," "fractional birth," "dismemberment" and "born-live" abortions—despite many medical professionals criticizing and opposing their apply. This fact canvass explains why individuals may seek abortions later in pregnancy, how often these procedures occur, how the concepts of viability and fetal pain play into this topic, and the various laws which regulate admission to abortions later in pregnancy.
Clarifying Pregnancy Dating: pregnancies are measured using gestational age (GA), calculated in days and weeks since the first day of the concluding menstrual menstruum (LMP). Since some people do not know the date of their LMP, ultrasound can as well exist used to summate GA. Post-fertilization or fertilization age refers to the time since the egg and sperm fused to create a fertilized egg. Fertilization occurs approximately two weeks after menses, thus gestational age by LMP predates fertilization historic period past ~2 weeks. By convention, gestational age is used to hash out pregnancy dating as most pregnant individuals know their LMP, however sure abortion regulations reference fertilization age instead.
What is a and then-called "late-term" abortion?
"Late term" abortion typically refers to abortions obtained at or afterwards 21 weeks, still it is not an accepted medical term, nor is there a consensus around to which gestational ages it refers. Members of the medical community have criticized the term "late-term" abortion, equally it implies abortions are taking identify later a pregnancy has reached "term" (37 weeks) or "late term" (>41 weeks) which is simulated. In fact, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has written that "late-term abortion" has no medical pregnant and should not be used in clinical or legal settings. As such, nosotros will refer to abortions occurring at ≥21 weeks gestation as abortions later in pregnancy, only it should be noted that 21 weeks is a largely capricious cutoff based on how the CDC collects information on abortions. Abortions at this phase in pregnancy are sometimes referred to as "afterwards abortions" by the medical community as well.
What is viability? Why does information technology matter for abortions subsequently in pregnancy?
Abortions later in pregnancy have been highly debated, in role considering some people believe that this stage of pregnancy abuts the fourth dimension effectually viability. In 1973, Roe v. Wade legalized abortion in the U.South., and in the procedure made "viability" the delineating factor in the abortion debate; before viability, a person has the right to obtain an abortion, whereas afterwards viability, the state tin restrict admission to ballgame in the involvement of protecting the potential for human being life, except in cases of health or life endangerment of the significant person.
The Supreme court made clear in Roe v. Wade that the courts are not in a position to assess when life begins and when viability has been reached, writing, "We need non resolve the difficult question of when life begins. When those trained in the respective disciplines of medicine, philosophy, and theology are unable to arrive at whatsoever consensus, the judiciary, at this point in the development of human being's knowledge, is not in a position to speculate as to the answer." ( Roe v. Wade ) Given viability is case dependent and is simply a possibility or probability of survival, rather than a guarantee of survival, the determination in Roe v. Wade left the right to an abortion after viability up to private states to determine.
In a subsequent Supreme Court instance on abortion, the courtroom divers viability as follows:
"Viability is reached when, in the judgment of the attention physician on the detail facts of the example before him, in that location is a reasonable likelihood of the fetus' sustained survival outside the womb, with or without artificial back up. Considering this point may differ with each pregnancy, neither the legislature nor the courts may proclaim one of the elements entering into the observation of viability – exist it weeks of gestation or fetal weight or any other single cistron – as the determinant of when the State has a compelling interest in the life or health of the fetus." Colautti v. Franklin (1979)
Viability depends on many factors, including gestational age, fetal weight and sex, and medical interventions available. While viability does not refer to a specific gestational historic period, it is often presumed at 24 weeks gestation, with "periviability" referring to the time around viability (twenty to 26 weeks gestation). For periviable births, the hospital at which the baby is delivered tin greatly affect viability, and the patient'southward insurance coverage may dictate where they tin seek intendance. Infants built-in in resource-rich settings take a higher likelihood of survival than those born in resource-poor settings. This is in part due to admission to neonatologists and maternal-fetal-medicine doctors, but also due to infirmary-specific policies; in a study of 24 bookish hospitals, agile handling for infants built-in at 22 weeks ranged from 0% to 100% depending on the hospital, showing that the criteria used to determine viability at i hospital may not be the aforementioned at another. If time allows and if the pregnant individual is clinically stable, they may be transferred to a facility meliorate equipped for neonatal resuscitation earlier delivery, however this is non ever possible. Further, insurance coverage and reimbursement for transfers in intendance varies past state and insurance plan.
At the time of Roe v. Wade , the Supreme Court wrote that viability "is ordinarily placed at about seven months (28 weeks), but may occur earlier, even at 24 weeks." With medical advances, extremely preterm infants can now survive at lower gestational ages than previously idea possible, particularly at hospitals with Level Iv neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). The question we come up up against is this: with viability possible at lower gestational ages, will abortions be prohibited at lower gestational ages also? Many favor leaving that decision up to the patient and their provider, given viability depends on the individual pregnancy. Others, including some policymakers, desire early gestational age limits on abortion, well before the possibility of viability. In subsequent sections, we outline policies that regulate the provision of abortions later in pregnancy, including gestational age restrictions.
How mutual are abortions later in pregnancy?
Abortions occurring at or after 21 weeks gestation are rare. Co-ordinate to the CDC's Abortion Surveillance Information, the vast bulk of abortions (91%) occur at or before 13 weeks gestation, while seven.7% occur from weeks 14 to 20 gestation, and merely 1.two% of abortions are performed at or after 21 weeks (Figure one). This amounts to approximately 5,200 abortions per year occurring at or afterwards 21 weeks, however this is an underestimate as only 33 reporting areas report abortions to the CDC by gestational historic period. The pct of abortions occurring at or earlier xiii weeks gestation has remained stable over the final few decades at 91-92%, however within this timeframe, more abortions are occurring earlier in pregnancy, at or earlier 8 weeks. This is likely in function due to the greater availability of medication abortions over the concluding 2 decades.

Figure i: The Vast Bulk of Abortions Occur Early on in Pregnancy
The CDC does not elaborate on the breakdown past gestational age for abortions occurring by 21 weeks, just information technology is likely that the vast bulk occur before long subsequently 21 weeks rather than in the later in the pregnancy. While very limited information exists on this issue, a study from 1992 estimated 0.02% of all abortions occurred after 26 weeks gestation (320 to 600 cases per year). This may overestimate electric current day numbers, given the abortion rate is currently at a historic low, and restrictions on abortions later in pregnancy have increased.
Why do people have abortions later in pregnancy?
Non-Medical Reasons: Individuals seek abortions later in pregnancy for a number of reasons. Equally part of the Turnaway study out of the University of California San Francisco, from 2008-2010 over 440 women were asked almost why they experienced delays in obtaining abortion care, if whatever (Figure 2). Most half of individuals who obtained an abortion afterward xx weeks did not suspect they were pregnant until later in pregnancy, and other barriers to intendance included lack of information nearly where to access an abortion, transportation difficulties, lack of insurance coverage and disability to pay for the process. This is unsurprising, given abortions can be cost-prohibitive for many; in a report from 2011-2012, the median cost of a surgical abortion at 10 weeks was $495, jumping to $1,350 at 20 weeks (range $750-$v,000) excluding the cost of travel and lost wages. Yet the Federal Reserve Lath found twoscore% of U.S. adults do not take enough in savings to pay for a $400 emergency expense, significant many individuals may demand to delay having an abortion until they can heighten the necessary funds.

Effigy 2: Many Factors Contribute to Delays in Obtaining Abortion Care
Additionally, of all the ballgame-providing facilities in the U.Due south., only 34% offer abortions at 20 weeks and merely 16% at 24 weeks, meaning individuals may need to travel a significant distance to notice an available, trained provider. Abortions at this phase besides typically crave 2 days to complete with inpatient intendance, as opposed to outpatient or at-habitation direction that is possible earlier in pregnancy.1 In the years since these data were collected, dozens of ballgame restrictions accept been enacted across the county, including mandated waiting periods; it is therefore possible that individuals seeking abortion today may face even more delays in care than these data reflect.
Fetal Anomalies: Individuals also seek abortions later in pregnancy due to medical reasons. With medical advances, many genetic fetal anomalies can be detected early in pregnancy; for example, chorionic villus sampling can diagnose Down syndrome or cystic fibrosis as earlier as 10 weeks gestation. Structural fetal anomalies, yet, are often detected much later in pregnancy. As part of routine care, a fetal anatomy scan is performed around 20 weeks, which entails ultrasound imaging of all the developing organs. Many structural anomalies are discovered at this time that would not accept been credible previously. A proportion of these are lethal fetal anomalies, pregnant that the fetus will almost certainly die before or shortly after birth, meaning the fetus may be nonviable.2 In these cases, many individuals wish to cease their pregnancies, rather than carrying the pregnancy until the fetus or newborn passes away. Very oftentimes these pregnancies are desired, making this conclusion exceedingly difficult for parents. Inadequate information exist to know how many abortions later in pregnancy occur due to fetal anomalies, merely a study by Washington University Hospital showed almost all women whose fetuses had lethal fetal anomalies chose to end their pregnancies.
A study of maternal fetal medicine (MFM) doctors—specialists who manage pregnancies with fetal anomalies— establish most agreed that termination of pregnancy due to a lethal fetal bibelot should be immune in all circumstances (76%). The majority (75%) hash out ballgame as a direction option soon after diagnosing a lethal fetal anomaly, but services for terminating pregnancies in these scenarios are limited. Just 40% of MFMs worked at healthcare centers offer abortions past 24 weeks for lethal fetal anomalies. An boosted 12% knew of available services <50 miles abroad.
Health Adventure to the Pregnant Person: Life threatening atmospheric condition may too develop subsequently in pregnancy. These include conditions like early severe preeclampsia, newly diagnosed cancer requiring prompt treatment, and intrauterine infection (chorioamnionitis) often in conjunction with premature rupture of the amniotic sac (PPROM). If these conditions arise before the fetus is viable, the pregnant private may pursue termination of pregnancy to preserve their ain health. If these atmospheric condition ascend later on the fetus is considered feasible, Roe v. Wade still protects the right for these individuals to obtain an abortion in cases of wellness or life endangerment, all the same it may exist hard to observe a provider for this service as previously mentioned. Typically every effort is fabricated to save the life of both the pregnant individual and the fetus, pursuing delivery rather than abortion.
How do states regulate abortions afterwards in pregnancy?
A few states have sought to expand access to abortions later in pregnancy. The New York Reproductive Health Act enacted in Jan 2019 expands protections for abortion providers and pregnant individuals who have abortions afterward 24 weeks in cases of health or life endangerment or lethal fetal anomalies. Virginia similarly proposed loosening restrictions on abortions afterward in pregnancy, by reducing the number of physicians who would need to approve an ballgame after 28 weeks gestation from three to one, and by broadening maternal exceptions to include more general threats to mental and physical health. This neb failed to pass, but sparked national word well-nigh regulation of abortions afterward in pregnancy.
Many states take directed their efforts in the contrary direction, aiming to increment restrictions on abortions subsequently in pregnancy. States most frequently do then past (one) placing gestational age limits on abortion, and/or (2) restricting the methods providers can apply to perform abortions later in pregnancy. In discussion of these laws, it is important to note that most policymakers are not clinicians, therefore many of the terms used to discuss abortions later in pregnancy are designed to communicate a political message, not a precise medical concept. In the Appendix, nosotros mention several terms written into policy and the law so that readers may be familiar with their meaning, but they are non medical terms.
Abortion bans past gestational age
43 states prohibit abortions after a certain point in pregnancy, with almost half of states prohibiting abortion at "viability" or when viability is oft presumed, at 24 weeks. Other states seek earlier gestational historic period limits on ballgame. For case, so-called "heartbeat" bans propose banning abortion subsequently the detectable presence of cardiac activeness as early on every bit 6 weeks gestation, months before viability. To date, all such "heartbeat" bans, along with others that seek to ban abortions before 20 weeks, are non in effect due to ongoing or resolved litigation. Nevertheless, some states have enacted abortion bans from twenty-22 weeks gestational historic period, using the rationale of fetal pain.
Fetal Pain
Many states restrict abortions at 22 weeks gestational age or 20 weeks post-fertilization, arguing the fetus has the ability to feel pain at this bespeak in evolution, contrary to medical show. A systematic review of literature on fetal pain found that pain perception is unlikely before weeks 29 or 30 gestational age. ACOG has found "no legitimate scientific information or data" that supports the exclamation that fetuses feel pain at 20 weeks post-fertilization, and the Regal Higher of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has likewise concluded fetal pain is non possible earlier 24 weeks, given immature encephalon development and neural networks.
Despite the medical evidence, policymakers take enacted gestational limits using the rationale that a fetus can experience pain at earlier stages in pregnancy. Mississippi bans ballgame at xx weeks gestation while abortion at 22 weeks gestation is banned by 17 other states (AL, AR, GA, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, NE, ND, OH, OK, SC, SD, TX, WV, WI). Additionally, thirteen states provide verbal or written counseling on fetal pain as role of pre-abortion counseling (AK, AR, GA, IN, KS, LA, MN, MO, OK, SD, TX, UT, WI) (Figure 3). Some states mandate this information be given to those seeking abortion later in pregnancy, while in others, this counseling is required at any stage of pregnancy. In Utah legislation was introduced, merely not passed, that would take required providers to administer "fetal anesthesia" during abortions later on in pregnancy. There is, nevertheless, no standard do for how to provide fetal anesthesia during abortions, nor is in that location adequate safety data on how this would affect pregnant individuals.
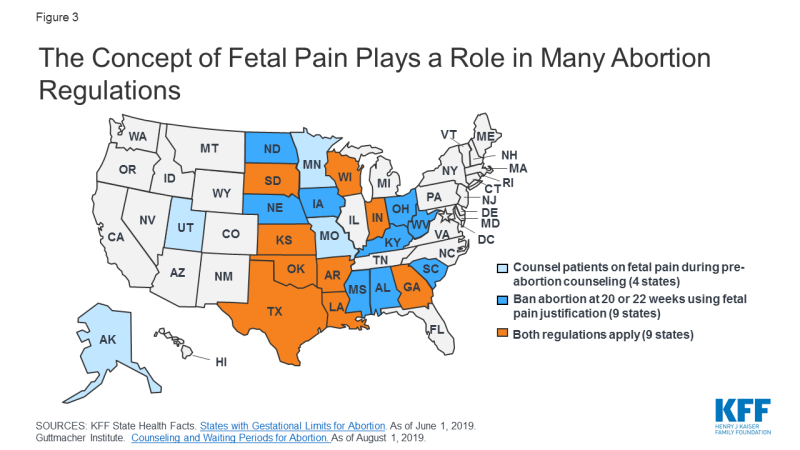
Effigy 3: The Concept of Fetal Pain Plays a Role in Many Abortion Regulations
Bans on abortion methods used later in pregnancy
Almost all abortions performed at ≥21 weeks are performed by a dilation and evacuation (D&E) procedure (93–95% per CDC data). This involves dilating the cervix and evacuating the pregnancy tissue using forceps, with or without suction. D&Es can be performed safely up to at to the lowest degree 28 weeks gestational age, and when compared to their alternative of labor induction, have been institute to be quicker and result in fewer complications; further, many women adopt surgical management as they will be sedated and do not have to undergo labor and delivery of the fetus.
Several states have sought to ban D&E procedures, which would significantly limit how providers are able to perform abortions subsequently in pregnancy. Currently, Mississippi and West Virginia have enacted D&E bans, while bans are temporarily enjoined in vi states and over 25 states accept attempted to laissez passer such legislation. xx states ban dilation and extractions (D&Xs), a rarely used abortion procedure also referred to equally an intact D&E or a "partial birth abortion" by policymakers (Appendix). In total, 21 states have enacted bans on abortion methods used later in pregnancy (Effigy four).
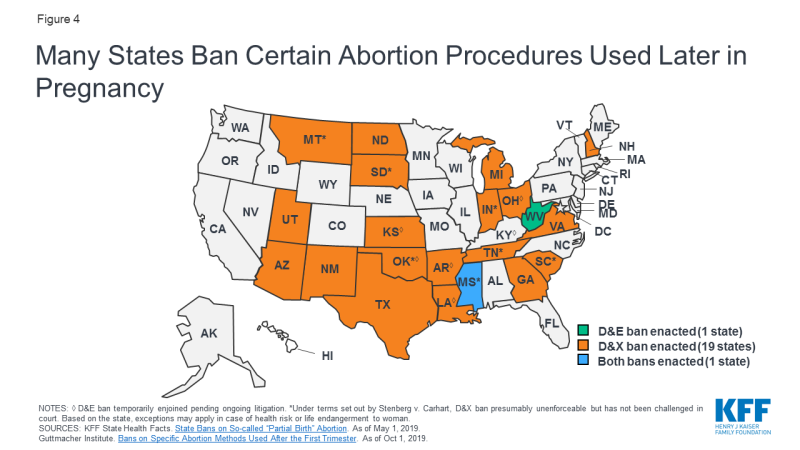
Figure iv: Many States Ban Certain Ballgame Procedures Used Later in Pregnancy
In addition to gestational historic period limits and method bans used for abortions later in pregnancy, it is important to call back these abortions are also field of study to the same regulations that apply for abortions earlier in pregnancy, including mandatory waiting periods and physician and infirmary requirements.
The authors would like to acknowledge Jennifer Karlin, MD, PhD (Academy of California, San Francisco) for her review of an earlier draft of this fact sheet.
Appendix
| Non-Medical Terminology Used to Describe Abortions in Policy and Constabulary | |
| Term | Clarification |
| Late-term abortion: | Non-medical term that typically refers to abortions occurring at or after 21 weeks gestational historic period, simply does non consistently refer to a specific gestational age cutoff. |
| Post-viability abortion: | Non-medical term used to refer to abortions occurring afterwards the fetus is considered viable, and sometimes used synonymously with late-term abortions. |
| Built-in-alive ballgame: | Non-medical term used to refer to the exceedingly rare circumstance in which a newborn shows signs of life after an abortion, including breathing, a beating center and voluntary motion. These cases are the subject of the proposed "Built-in-Alive Abortion Survivors Protection Human activity," mandating healthcare workers provide care to infants who testify signs of life subsequently an attempted ballgame. |
| Fractional birth abortion: | Non-medical term often used to refer to a rarely used abortion procedure chosen dilation and extraction (D&X, also known an intact D&E). Has sometimes been used to refer to all dilation and evacuations (D&Es), the most common ballgame process used from 14-28 weeks gestational historic period. |
| Dismemberment ballgame: | Non-medical term sometimes used to refer to D&Es. |
| NOTES: KFF does not endorse use of these terms. | |
williamsontobt1980.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/fact-sheet/abortions-later-in-pregnancy/
0 Response to "Percentage of Aborted Babies That Are Endangering the Mother"
Post a Comment